Written by: The Midland Certified Reagent Company
Read below to see the importance of an oligonucleotide.
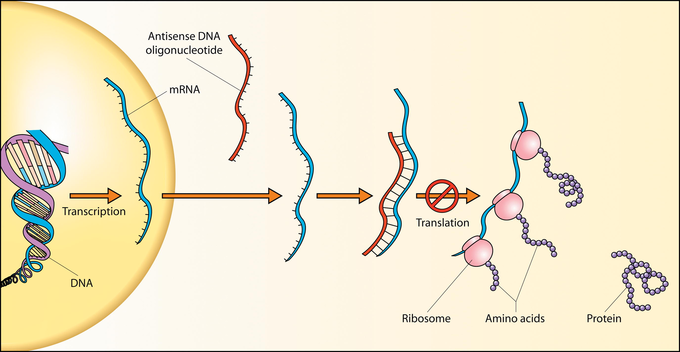
The structure of both RNA and DNA synthesis are somewhat similar with some minor differences in the bases. Oligonucleotides are nucleic acid polymers that play a role within the synthesis of both RNA and DNA. Here is a brief rundown on how oligonucleotides play a crucial role in research, forensics, and genetic testing.
What Are Oligonucleotides?
Oligonucleotides are polymers that are made up of numerous nuclelotides and are designed for the specific purpose of hybridizing DNA or RNA sequences in a controlled setting. Usually handled by trained laboratory workers, these oligos have played a large role in detecting specific sequences when needed. Derived from the Greek word “oligo” which means small or few amounts, these probes continue to revolutionize the procedures performed in a lab. Some examples of these procedures include: DNA micro arrays and ASO analysis.
Their Purpose
Oligonucleotides can detect specific sequences when neeed.They are bound to a fluorescent label and utilized to allocate specific segments of DNA or RNA, prior to both DNA and RNA synthesis cycles. While primarily synthesized in a laboratory they are created to assist in determining specific modules of cellular strands in order to pinpoint exactly what the scientist is looking for.
The Bottom Line
Oligonucleotides continue to transcend the world of science and are constantly being researched in the hopes that there will be advanced modifications that will allow scientists to further enhance their scope of practice. It wouldn’t be surprising to expect that in the coming years as technology tends to move at a rapid pace.